Design Basis
The main basis for mold design is the plastic product drawings and physical samples provided by the customer. Mold designers must conduct a detailed analysis and understanding of the product drawings and physical samples. At the same time, when designing the mold, they must check all the following items one by one:
1. Dimensional Accuracy and the Correctness of Its Related Dimensions
According to the specific requirements and functions of the plastic product in the entire product, determine which type its appearance quality and specific dimensions belong to. Generally, there are three situations. The first is the plastic products with high requirements for appearance quality and low requirements for dimensional accuracy, such as the outer parts of toys. Their appearance must be beautiful. Except for the assembly dimensions, the other dimensions only need to fit well and have a realistic shape. The second is the functional plastic products with strict dimensional requirements. Their dimensions must be within the allowable tolerance range, otherwise, it will affect the performance of the entire product. Such products include plastic gears, etc. The third is the plastic products with strict requirements for both appearance and dimensions, such as plastic parts for cameras, plastic optical lenses, etc. For the strictly required dimensions, if the tolerance of certain dimensions exceeds the standard requirements, a specific analysis should be carried out to see if appropriate adjustments can be made during the mold testing process to meet the requirements.
2. Whether the Demoulding Draft Angle is Reasonable
The demoulding draft angle is directly related to the demoulding and quality of the plastic product, that is, it is related to whether the injection process can proceed smoothly. Therefore, it is required that the plastic product has a sufficient demoulding draft angle. The direction of the demoulding draft angle should be suitable for the parting surface of the plastic product during molding or the parting surface of the mold. Otherwise, it will affect the appearance of the product and the accuracy of the wall thickness dimension, and even affect the strength of certain parts of the plastic product.

3. Wall Thickness of the Product and Its Uniformity
The wall thickness of the plastic product should be appropriate and have a certain degree of uniformity. If the wall thickness is too thick or the uniformity of the wall thickness is poor, it will directly affect the molding quality of the product and the deformation after molding, prolong the molding cycle, and even increase the cost of the product.
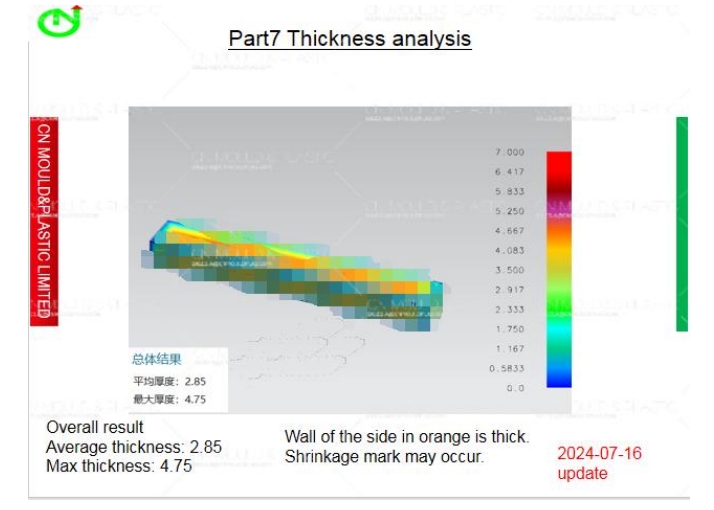
4. Types of Plastics
Various different plastics have their commonalities and also their respective characteristics. When designing the mold, the influence and requirements of the plastic characteristics on the mold must be considered so as to adopt corresponding design schemes. Therefore, it is necessary to fully understand the name of the plastic, its grade, the manufacturer, and the shrinkage rate, etc. For example, when molding plastics reinforced with glass fibers, the mold cavity and core should have high hardness and wear resistance. When molding flame-retardant plastics, the cavity and core must have anti-corrosion performance to prevent the corrosion of the mold by the corrosive gas emitted during the injection process. In addition, the colors and shrinkage rates of plastics produced by different manufacturers are also not the same.
5. Surface Requirements
The surface requirements of plastic products refer to the surface roughness and surface texture requirements of plastic products. The surface roughness of the mold forming surface is different for transparent and non-transparent products. For transparent products, the surface roughness of the cavity and core is required to be the same. For non-transparent products, the surface roughness of the cavity and core can be different. The mold parts forming the decorative surface should have higher roughness requirements, while for the non-decorative surface, the mold surface can be rougher without affecting the demoulding.
The surface roughness requirements of plastic products should be determined according to the surface quality requirements of the products, and can be selected according to the aviation standard HB6841-93 (Technical Requirements and Evaluation Methods for Surface Roughness Samples of Plastic Mold Cavities and Plastic Samples).
The surface texture requirements of plastic products should be selected according to the plastic texture samples provided by professional manufacturers. When designing a mold with surface texture requirements, special attention should be paid to the influence of the side surface texture on the demoulding of the product, and the demoulding draft angle of the side surface should be 2°~3°.
6. Color of the Plastic Product
Under normal circumstances, the color has no direct impact on mold design. However, in the case of thick-walled and large-sized products, it is easy to produce uneven color, and the darker the color of the product, the more obvious the product defects will be exposed.
7. Whether There is Post-treatment After the Plastic Product is Moulded
Some plastic products need to be heat-treated or surface-treated after molding. For products that need heat treatment, the influence of heat treatment on their dimensions should be considered when calculating the molding dimensions. For products that need surface treatment, such as products that need surface electroplating, if the products are small and the production batch is large, an auxiliary runner must be considered to connect the products as a whole. After the electroplating process is completed, the products are separated from the auxiliary runner.
8. Production Batch of the Product
The production batch of the product is one of the important bases for mold design. Therefore, the customer must provide a range for the monthly batch, annual batch, and total batch so that when designing the mold, the number of cavities of the mold, the size of the mold, the material selection of the mold, the mold life, etc. can be adapted to the batch.
9. Specifications of the Injection Molding Machine
When receiving an order from the customer, the customer must clearly state the specifications of the injection molding machine to be used, so as to serve as the basis for mold design. The specifications of the injection molding machine provided should include the following contents:
(1) Model and manufacturer of the injection molding machine
(2) Maximum injection volume (maximum injection amount) of the injection molding machine;
(3) Clamping force of the injection molding machine;
(4) Spherical radius of the injection molding machine nozzle and the diameter of the nozzle hole;
(5) Diameter of the positioning hole of the injection molding machine;
(6) Inner spacing of the tie bars of the injection molding machine;
(7) Mould capacity of the injection molding machine (allowable maximum and minimum closing heights of the mold);
(8) Ejection mode of the injection molding machine (hydraulic ejection or mechanical ejection, as well as the position of the ejection point and the diameter of the ejector pin);
(9) Mold opening stroke and maximum opening distance of the injection molding machine;
(10) If necessary, the ejection stroke and ejection force of the injection molding machine should also be provided.
10. Other Requirements
When placing an order, in addition to providing the necessary design basis, some customers may even put forward some specific requirements for the mold, such as the number of cavities and the types of products molded in the same mold, the form of the gate, the form of the mold (two-plate mold or three-plate mold), the ejection mode and ejection position, the operation mode (manual, semi-automatic, fully automatic), the surface roughness of the cavity and core, etc. They may even put forward specific requirements for the grade of the steel used for the cavity and core and the hardness after heat treatment.
The above contents must be carefully considered and checked by mold designers to meet the requirements of customers.

 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Svenska
Svenska  norsk
norsk