The presence of internal stress reduces the mechanical properties of injection molded products or leads to anisotropy, resulting in poorer durability during use. Especially when the usage conditions change (e.g., temperature increase, solvent exposure, mechanical force application), the product may crack or deform. Some transparent products might exhibit whitening, cloudiness, or surface "silver streaks".
Whether internal stress exists in an injection molded product can be checked using the following methods:
(1) Polarized Light Inspection: Use a transparent product as a sample and place it between polarizing lenses. Observe the area of the colored bands appearing on the product surface through the lenses. A larger area of colored bands indicates a greater range of internal stress within the product.
(2) Solvent Immersion Method: Immerse product samples in a solvent and record the time until half of the samples crack. A longer cracking time indicates lower internal stress in the product. For testing:
PS, PC, PSU, PPO can use carbon tetrachloride.
Polyolefins can use surfactants.
Other products can use solvents such as methanol, ethanol, etc.
To reduce or disperse internal stress in the product, the following measures can be taken:
Plastic Material
Use pure plastic material with minimal impurities.
Select plastic types (grades) with high molecular weight, narrow molecular weight distribution, and good processing properties.
When preparing blended materials, ensure uniform mixing of all components.
For crystalline plastics, add an appropriate amount of nucleating agent (e.g., add a suitable amount of hexanedioic acid to PP plastic).
Product Design
When designing wall thickness, strive for uniformity across all parts of the product. In areas with significant differences in wall thickness, avoid right-angle transitions; instead, use arc transitions, trapezoidal transitions, or hollow out one side (Figure 1-1).
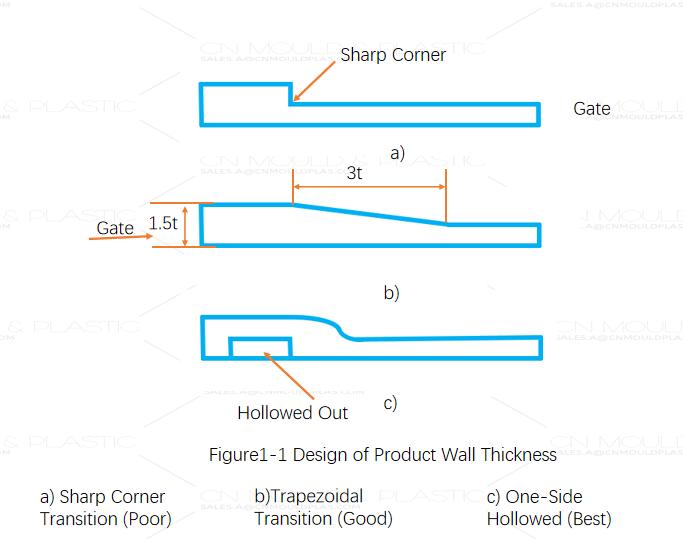
The product shape should preferably adopt streamlined, curved, or double-curved surfaces, avoiding sharp corners. When designing round holes, consider using an elliptical shape appropriately.
If metal inserts are required inside the product, preferably use copper or aluminum for the insert material, and preheat the inserts before molding.
Mold Design
Without affecting the product's appearance, the mold's draft angle should be as large as possible. The ejection area of the mold's ejection system should be as large as possible.
The mold should preferably use small gates and large runners to shorten injection time and reduce injection and holding pressure.
The mold's cooling system should ensure consistent cooling levels in the moving half and fixed half. If allowed, the mold cooling temperature can be set appropriately higher.
Process Conditions
Appropriately increase the heater barrel temperature; appropriately decrease the injection pressure.
Use fast filling speed and low holding pressure.
Slow down the cooling rate of the product within the mold.
For demolded products, heat treatment (annealing) can be used to improve polymer crystallization perfection and alleviate internal stress.

 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Svenska
Svenska  norsk
norsk 




