Product Description
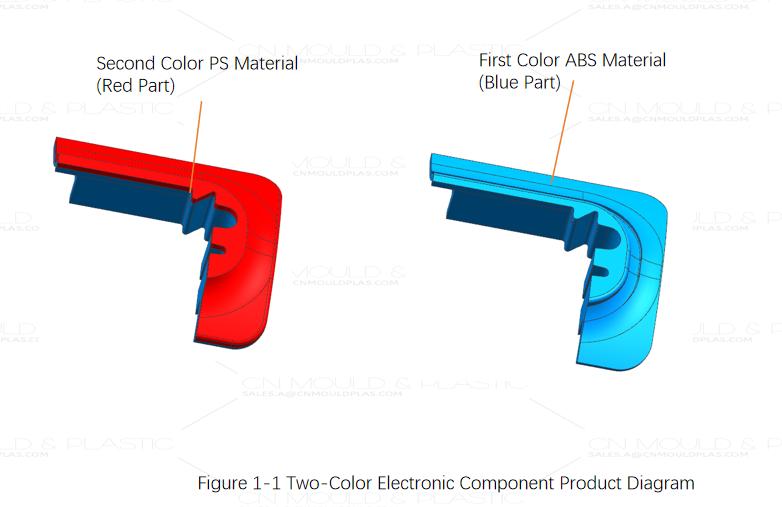
Figure 1-1 shows a two-color product diagram of an internal part for a household appliance. The product has an average wall thickness of 1.2mm and overall dimensions of 6.1mm x 18.2mm x 49.6mm. The green section represents the first shot material, ABS, with a weight of 0.97g. The orange section represents the second shot material, PS, with a weight of 0.38g. The mold is required to produce 8+8 cavities per cycle. It demands high aesthetic standards for the product and requires an injection cycle time of 14 seconds, classifying it as a precision two-color mold.
Design Key Points
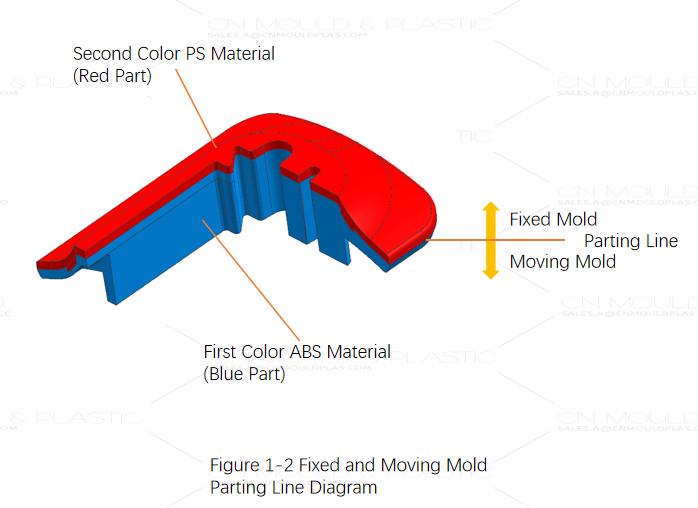
Parting Line and Ejection Direction
The product structure is very simple. The second shot PS material can be entirely formed in the fixed half (cavity side). This product fully complies with the most basic principle of simple two-color mold design: the product shapes in the fixed half are different, while the moving half (core side) shapes are identical. The parting line is also relatively simple: it is regular, following the product's maximum outer contour where the fixed half and moving halves meet directly, as shown in Figure 1-2.
Gate Setting
This two-color mold is designed for use with an H-type two-color injection molding machine. Since the weight of this two-color product is relatively small, the required tonnage of the two-color injection machine is also relatively small, and the shot volume cannot be large. Its auxiliary nozzle and main nozzle are perpendicular to each other, with the second shot auxiliary nozzle located on the top side (sky side) of the machine. However, because the moving platen of this injection machine is not equipped with a rotary table, the rotating moving half core solution was adopted for designing this two-color mold. By rotating the moving half cores, the conversion between cores in two different positions is achieved, thus completing the two-color injection molding of the product. The second shot material for this product is not a soft elastomer but rather PS, a rigid plastic. The product is relatively small, and the shot volume for the second shot material is not large. As long as the adhesion between the first and second shot materials is good, and the injection temperature of the second shot material is not too high, it has minimal impact on the two-color mold design.
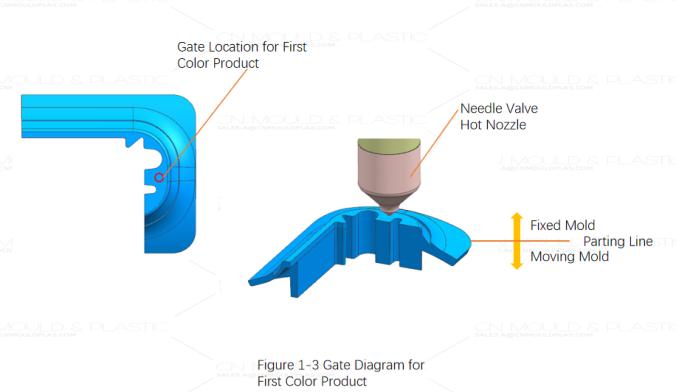
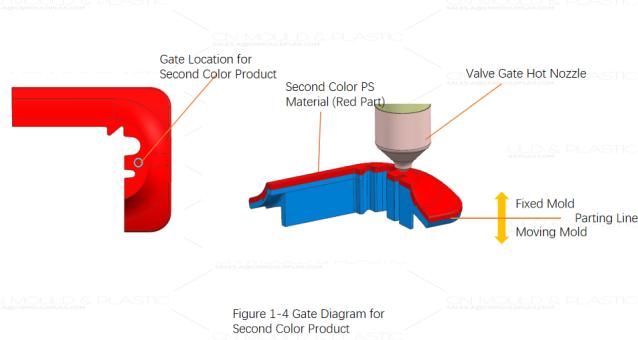
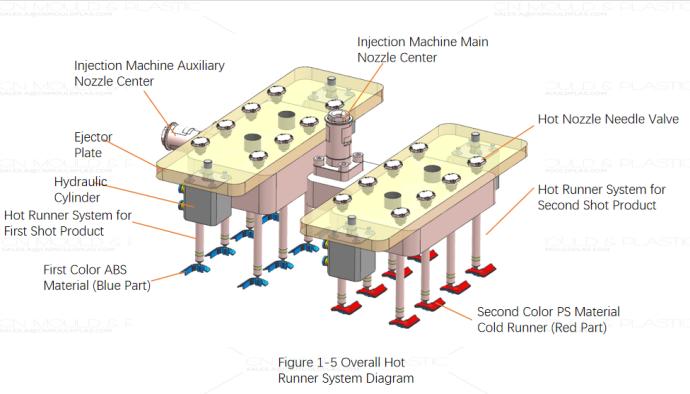
Based on the product characteristics – small size, a mold cycle time of 14 seconds, and the requirement for fully automatic production – it was decided to use valve-gated hot nozzles for both the first and second shot materials, gating directly on the product surface. Figure 1-3 shows the gate for the first shot ABS material. The gate vestige in this location can be covered by the second shot material, not affecting the product's appearance. Figure 1-4 shows the gate for the second shot PS material. Although it is on the product's outer surface, the use of a valve-gated hot nozzle and the intentional design of a flat surface on the product mean the gate vestige has little impact on the product's appearance. Figure 1-5 shows the overall hot runner system layout for this mold. Due to the product's small size and the high number of cavities, space within the hot runner system is limited. When designing the hot runner, the valve pins of the hot nozzles are all fixed to a single ejector plate, using a combination of a hydraulic cylinder and the ejector plate to control the opening and closing of the hot nozzle valve pins.
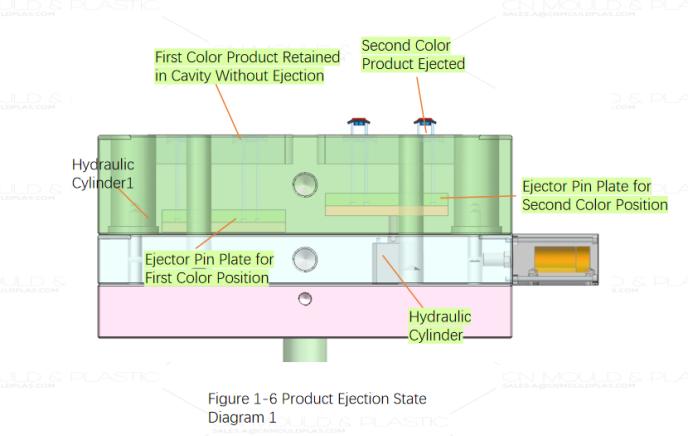
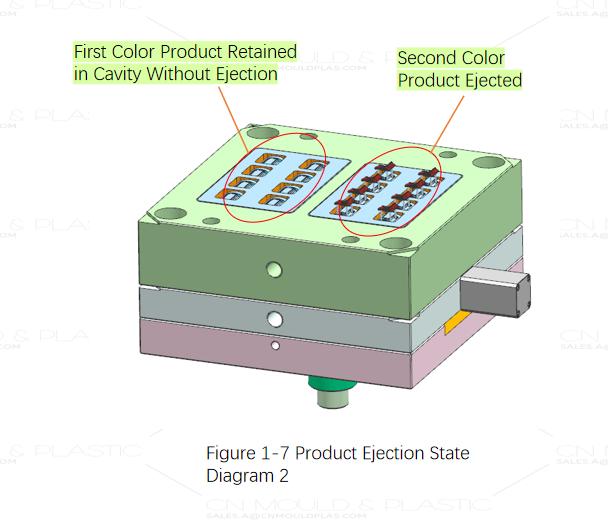
Product Ejection
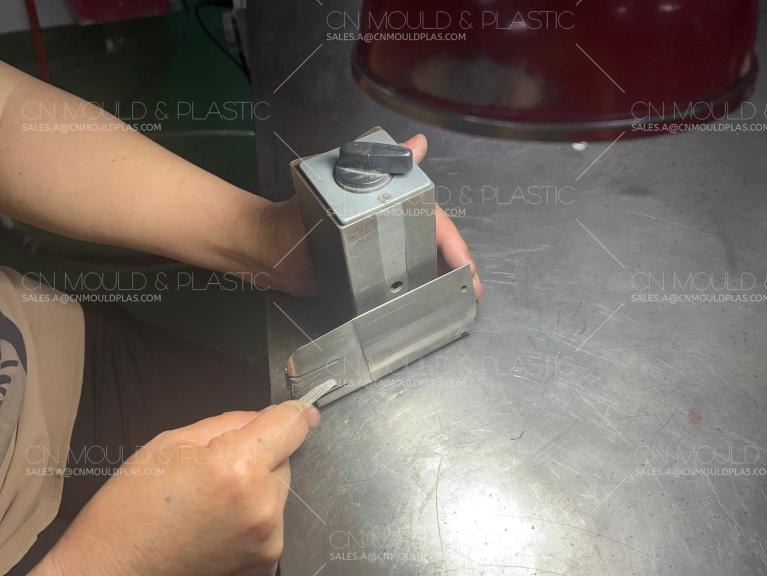
The product ejection for this mold is relatively straightforward, simply using ejector pins and blade ejector pins to eject the product at the second shot position. Figures 1-6 and 1-7 show the product ejection status. After the second shot PS material injection is completed, the mold opens. Hydraulic cylinders installed internally at the second shot position of the mold actuate the ejector plate and ejector retainer plate, ultimately driving the ejector pins and blade ejector pins fixed to the plates to eject the product. During this process, the first shot product remains on the moving half core and does not participate in the ejection.

 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Svenska
Svenska  norsk
norsk 










