I.Section 1 Basic Knowledge of Quality Inspection Work
Overview Firstly, one should be familiar with the specified requirements (quality standards) for one or more characteristics being inspected, and convert them into specific quality requirements, sampling and inspection methods, determine the measuring devices to be used. Through the concretization of the requirements (quality standards), relevant personnel can be made familiar with and master what kind of products are qualified products. The inspection is divided into the following steps.
1. Measurement Measurement refers to quantitatively (or qualitatively) measuring, inspecting, testing or gauging one or more characteristics of the product according to the determined measuring device or physical and chemical analysis instrument.
2. Comparison Comparison means comparing the inspection results with the specified requirements (quality standards), and then observing whether each quality characteristic meets the specified requirements.
3. Judgment Quality management has both principles and flexibility. There are conformity judgments and suitability for use judgments for the quality of the inspected products. The conformity judgment is to determine whether the inspected product is qualified or unqualified according to the comparison results. The conformity judgment is the function of the inspection department. The suitability for use judgment is to further confirm whether the product or raw material judged as unqualified through the conformity judgment can be used. The suitability for use judgment is not the function of the inspection department, but the function of the technical department. Necessary tests must be carried out before making a suitability for use judgment on the raw materials. The suitability for use judgment can only be made when it is confirmed that the unqualified quality characteristic does not affect the final quality of the product.
4. Handling The handling stage of the inspection work includes the following contents.
① For a single product, the qualified one is transferred to the next process or put into storage. The unqualified one is subject to a suitability for use judgment or is handled through rework, repair, downgrading, scrapping and other means.
② For batch products, according to the inspection results, analyze and make decisions such as acceptance, rejection or special procurement for handling.
5. Recording Carefully record the relevant measured data according to the format and requirements of the record. The quality records are controlled according to the requirements specified in the quality system documents. There should be corresponding quality records for the handling of unqualified products, such as rework notice, non-conforming product notice, etc.

II. Classification of Inspections
1. Classification according to the Sequence of the Production Process
(1) Incoming Inspection: It includes the incoming inspection of outsourced and purchased parts. According to the quality requirements of the outsourced and purchased parts and the degree of influence on the product quality characteristics, the outsourced and purchased parts are divided into three categories: A, B, and C, and different treatments should be given during inspection.
(2) Process Inspection
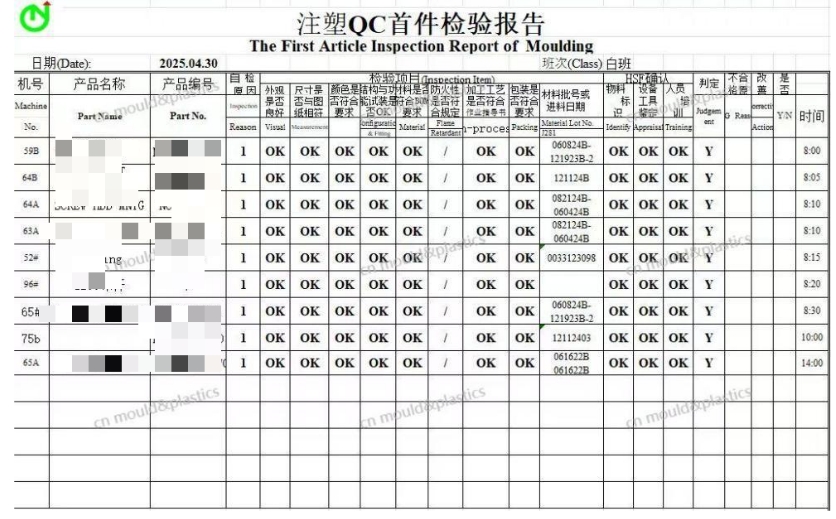
① First Article Inspection. It is the inspection of the first or the first few products manufactured at the start of production or after the adjustment of process factors (adjustment of processes, fixtures, equipment, etc.). The purpose is to detect the systematic factors in the process as early as possible and prevent the batch scrapping of products.
② Patrol inspection. Also known as mobile inspection, it is the supervisory inspection carried out by the inspector on the product quality and processing technology of relevant processes at a certain time interval in the production site. The inspection items and responsibilities that the mobile inspector should perform in the process inspection are as follows.
a. The key point of the mobile inspection is the key processes. The inspector should be familiar with the quality requirements, inspection methods and processing technology of the quality control points within the inspection scope, and is responsible for whether the processed products meet the quality requirements and the requirements specified in the inspection instructions, and also has the responsibility to supervise the implementation of the process;
b. Do a good job in the special storage and handling of the qualified products, unqualified products (rework products) and waste products after inspection;
c. Completion Inspection The completion inspection is a comprehensive inspection of a batch of completed products of this process. The purpose of the completion inspection is to pick out the unqualified products so that the qualified products can continue to flow into the next process. The process inspection is not simply a matter of quality control, but should be combined with quality control, quality analysis, quality improvement, process supervision, etc., and focus on checking the effectiveness of the leading elements of the quality control points.
(3) Final Inspection The final inspection is also called finished product inspection, and its purpose is to ensure that unqualified products do not leave the factory. The finished product inspection should be carried out according to the regulations of the finished product inspection instructions. The inspection of a large number of finished products generally adopts the method of statistical sampling inspection. All the finished products that fail the inspection should be returned to the workshop for rework, repair, downgrading or scrapping. The products that have been reworked or repaired must be inspected for all items again. The inspector should make inspection records of the reworked and repaired products to ensure the traceability of the product quality.
2. Classification according to the Inspection Location According to the inspection location, it can be divided into centralized inspection, on-site inspection and mobile inspection.
3. Classification according to the Inspection Method According to the inspection method, it can be divided into physical and chemical inspection, sensory inspection, and experimental use identification.
4. Classification according to the Quantity of Inspected Products According to the quantity of inspected products, it can be divided into full inspection, sampling inspection and exemption from inspection.
5. Classification according to the Data Nature of Quality Characteristics
① Measurement Value Inspection It is necessary to measure and record the specific values of quality characteristics, obtain measurement value data, and judge whether the product is qualified according to the comparison between the data value and the standard
② Count Value Inspection In the industrial production process, in order to improve production efficiency, limit gauges (such as plug gauges, caliper gauges, etc.) are often used for inspection, and the obtained quality data are the number of qualified products, the number of unqualified products and other count value data, and the specific values of quality characteristics cannot be obtained.
6. Classification according to the Inspectors According to the inspectors, it can be divided into self-inspection, mutual inspection and special inspection.
III. Commonly Used Abbreviations of Quality Inspection English
IQC (incoming quality control): Incoming Quality Control
PQC (process quality control): Process Quality Control
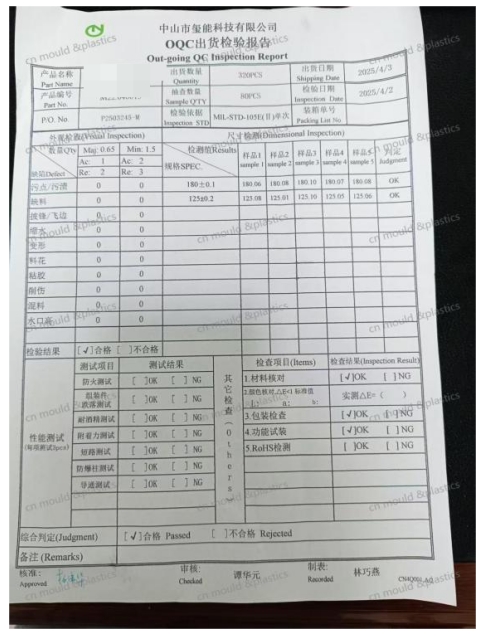
OQC (outgoing quality control): Outgoing Quality Control
OBA (open box audit): Open Box Audit
FQC (final quality control): Final Quality Control
SQA (source/supplier quality control): Supplier Quality Assurance
QE (quality engineering): Quality Engineering
MRB (material review board): Material Review Board
SPC (statistics process control): Statistical Process Control
QA (quality assurance): Quality Assurance
FA (failure analysis): Failure Analysis
AQL (acceptable quality level): Acceptable Quality Level
CR (critical): Critical, Fatal
MJ (major): Important, Main
MN (or MI) (minor): Minor, Slight
(CR, MJ, MN are usually used to indicate the importance of inspection items and the severity of defects)

 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Svenska
Svenska  norsk
norsk