Threaded fasteners are widely used in various industries, and their failure can have serious consequences. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the failure modes and causes of threaded fasteners to improve product quality and safety.
Failure Modes of Threaded Fasteners:
Common failure modes of threaded fasteners include:
1. Assembly Tensile Fracture:
* Low friction coefficient of the contact surface.
* Excessive torque applied during tightening or pre-tightening.
* Misalignment between the socket and the thread when applying torque.
* Excessive speed when applying torque.
* Insufficient performance strength of the part itself.
* Perpendicularity tolerance between the tightening surface and the thread center line is exceeded.
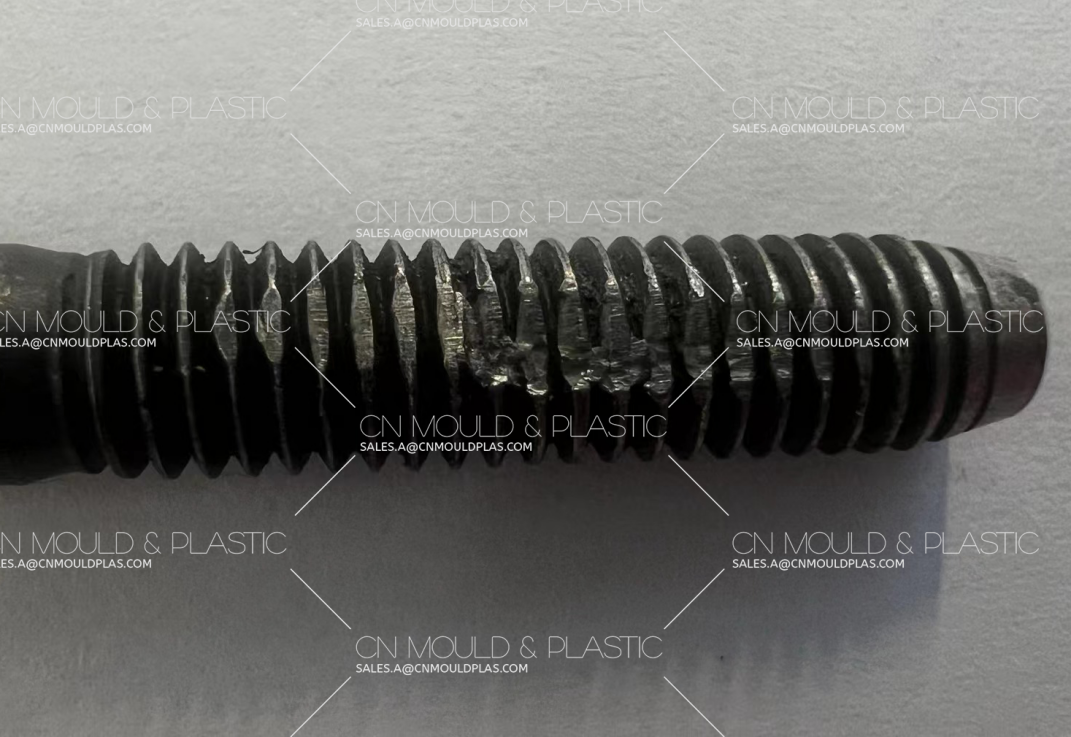
2. Thread Shearing Fracture:
* The thread is stuck during tightening.
* The cross-section of the screw is blocked, such as insufficient effective thread depth of the blind hole nut.
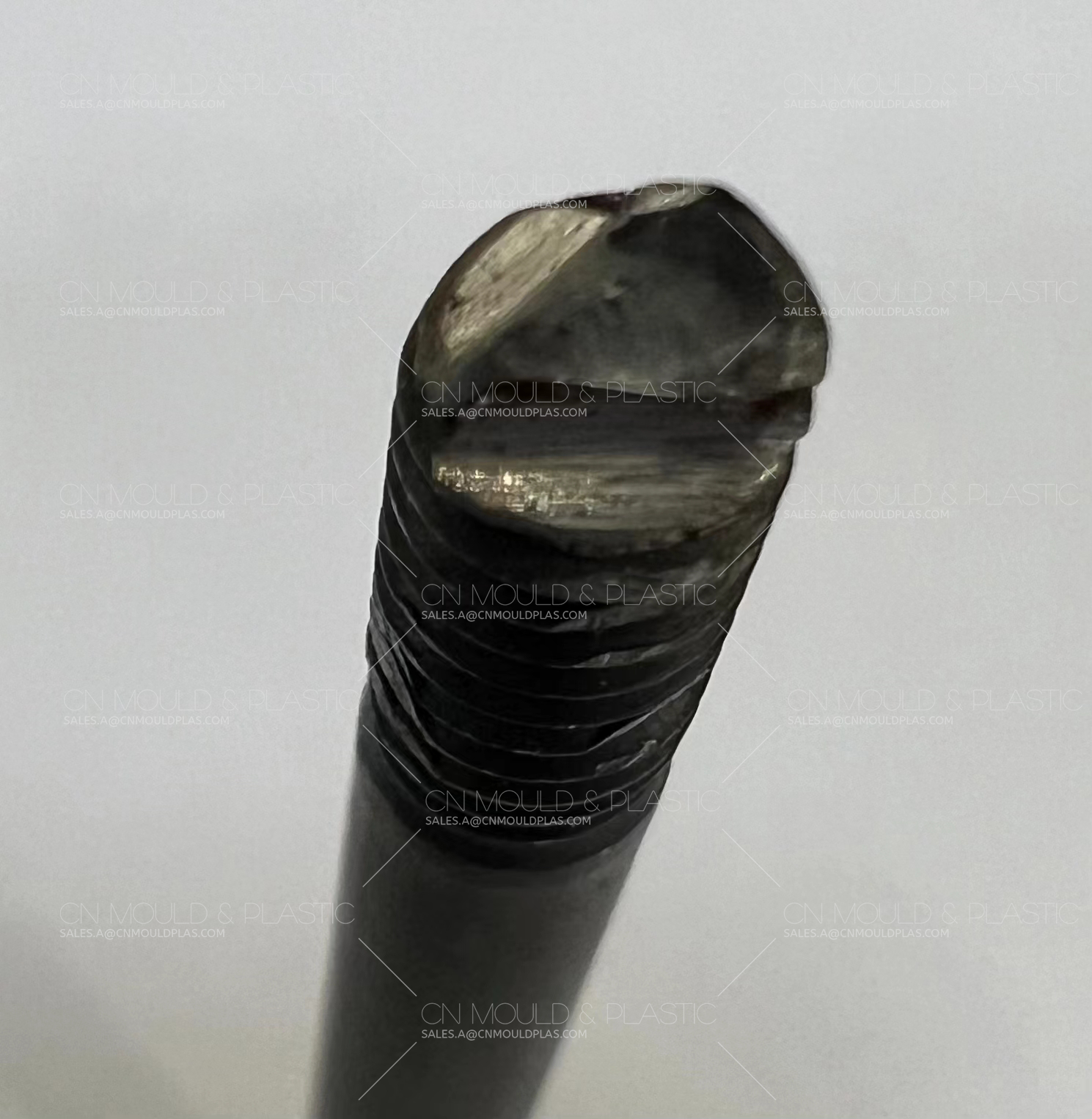

3. Stress Concentration Area Failure After Use:
* The fillet between the head and the shank is too small.
* Defects in the plastic streamline of the head during cold heading of the bolt.
* Perpendicularity tolerance between the mating surface and the bolt is exceeded.
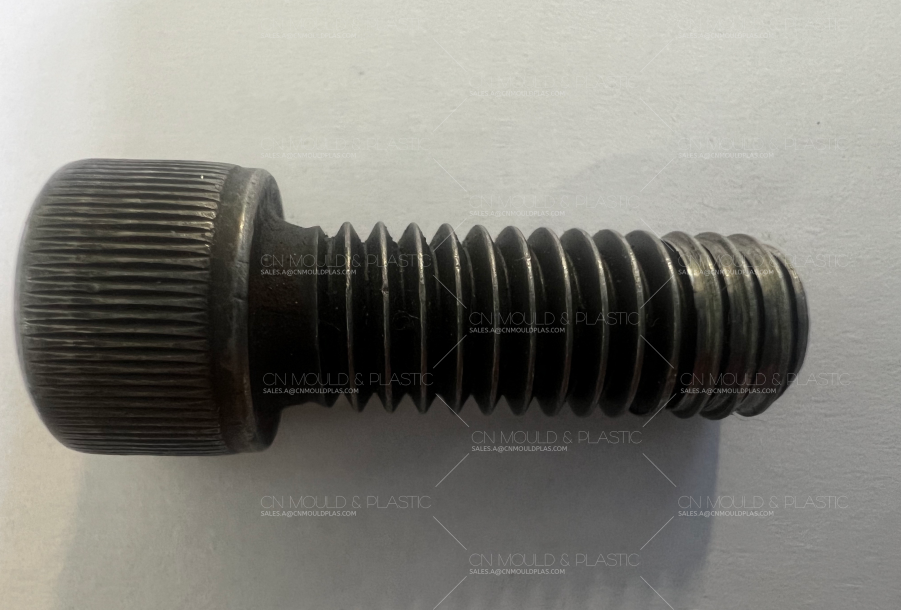

4. Fatigue Fracture:
* Insufficient preload.
* Excessive clamping force attenuation.
* Bolt size and performance are unqualified.
* The mutual matching, assembly environment, and working conditions of the parts cannot meet the design requirements.
5. Delayed Fracture:
6. Part Torque Alarm:
* Unreasonable assembly torque control range of the part.
* The actual torque is higher than the upper control limit or lower than the lower control limit after assembly.
* No pre-tightening to the preset angle, torque reaches the upper limit alarm.
* Normal assembly, torque lower limit alarm.
7. Thread Stripping:
* Decarburization of threads.
* Unreasonable thread size matching.
* Improper assembly method.
* Too small thread friction coefficient.
* Pitch and angle variation of the bolt and nut.
Prevention Measures:
To prevent threaded fastener failure, the following measures should be taken:
* Select suitable threaded fasteners and ensure their quality meets the requirements.
* Install threaded fasteners correctly and follow the corresponding operation specifications.
* Regularly inspect and maintain threaded fasteners, and promptly find and handle potential failure hazards.
By taking the above measures, the service life and safety of threaded fasteners can be effectively improved.


 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Svenska
Svenska  norsk
norsk 






