Properties that Plastic Mold Steels Should Possess
Ⅰ. Service Properties of Plastic Mold Steels
1. Hardness
Hardness is an important performance index required for molds. During operation, the mold should be able to maintain its dimensions and shape without rapid changes under the action of compressive stress, so as to maintain the precision and usability of the mold. Therefore, the heat-treated mold should have sufficient hardness to ensure that the mold has sufficient stiffness.
2. Wear Resistance
During operation, the mold has to bear considerable compressive stress and friction due to the filling and flowing of plastics. It is required that the mold can still maintain its dimensions and shape unchanged under such conditions to ensure that the mold has a sufficient service life. Especially when forming hard plastics or plastics reinforced with glass fibers, there is a higher requirement for wear resistance. The wear resistance of the mold depends on the composition, structure, and heat treatment hardness of the steel used. Therefore, increasing the hardness of the mold is beneficial to improving its wear resistance. However, when the hardness reaches a certain value, the influence of hardness on wear resistance becomes less obvious.
3. Strength and Toughness
The mold has to bear impact, bending, and shear stresses, etc. during operation, and it is often damaged (locally or severely) due to insufficient strength and toughness. Therefore, enabling the mold to have sufficient strength and toughness is beneficial to extending the service life of the mold and ensuring its safe use.
The grain size of the steel, the quantity, size, and distribution of carbides in the steel, as well as the amount of austenite, etc., all have a great influence on the strength and toughness of the steel. As the grain size in the steel increases and the unevenness of carbide distribution increases, the strength of the steel decreases, and it also has an adverse effect on its toughness. Therefore, according to the service conditions and performance requirements, reasonably selecting the chemical composition, structural state, and heat treatment process of the steel used for the mold can meet the requirements of the mold for its strength and toughness.
4. Corrosion Resistance
When forming plastic products such as polyvinyl chloride or those with additives like flame retardants, corrosive gases are decomposed during the thermoforming process, which has a strong corrosive effect on the mold. Therefore, for the molds used in the production of such plastic products, in addition to requiring the mold materials to have certain hardness, strength, and wear resistance, they also need to have a certain degree of corrosion resistance.
Ⅱ. Machinability of Plastic Mold Steels
1. Machinability
Machinability refers to hot working properties such as rolling, and cold working properties in the forms of cutting, grinding, etc., as well as etching processing performance. For plastic molds, their polishing performance should especially be considered. The above properties are related to the chemical composition of the steel, the quality of smelting, the structural state, and the contents of sulfur and phosphorus.

2.Heat Treatment Deformation
The requirements for the dimensions and shapes of molds are relatively strict. When the mold undergoes the final heat treatment after finishing, it is required that the changes in the dimensions and shapes of the mold are as small as possible. Therefore, it is required that the mold materials used have small deformation during heat treatment, and at the same time, they should have a sufficiently wide quenching temperature range to reduce the occurrence of overheating or insufficient quenching temperature.
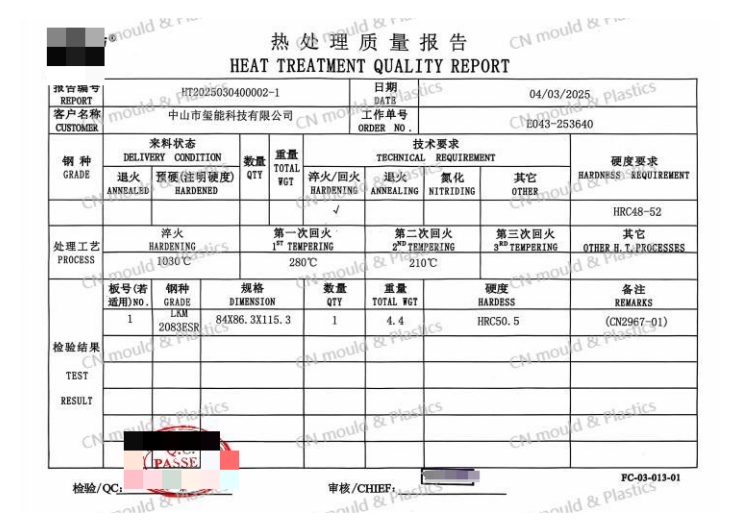
3.Hardenability and Quenchability
Hardenability is mainly related to the chemical composition of the steel, especially the carbon content. In addition to being related to the chemical composition of the steel, quenchability is also related to the original structure of the steel before quenching. According to the service conditions and functions of the mold, the requirements for its hardenability and quenchability have different emphases.
4.Decarburization Sensitivity
During heat treatment, decarburization occurs on the surface of the mold, which reduces the mechanical properties of the surface layer of the mold, especially having a greater impact on the surface wear resistance. Therefore, it is required that the decarburization sensitivity of the mold steel is as low as possible.

 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Svenska
Svenska  norsk
norsk