Pad printing utilizes the principle of intaglio printing. The tools include a silicone rubber pad, a printing plate (made of steel or fiber) with a screened pattern, and ink. It can print various fine lines, fonts, and patterns, and even four-color halftone images. Ideal printing effects can still be achieved regardless of whether the surface of the printed product is concave, convex, or irregular.
I. Process Flow Chart of Pad Printing
Pattern Design → Output of Film → Engraving of Steel Plate → Installation of Pad Printing Machine and Steel Plate → Installation of Cleaning and Ink Scraping System (Ink Tray, Scraper) → Preparation of Ink → Debugging of Pattern Pad Printing Effect → Pad Printing Production → Inspection → Packaging
II. Pad Printing Equipment
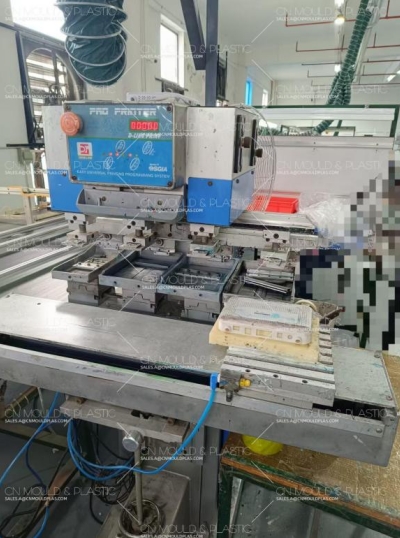
1. Pad Printing Machine
The pad printing machine is the core of pad printing production. It uses compressed air as the original power and controls the movement of the rubber pad and pad printing actions (such as the number of prints) through electrical signals to print single-color or multi-color patterns by overprinting. It can perform 1 to 3 times of flowing printing, 1 to 2 times of color turntable printing, and 2 to 6 times of color push plate printing. Select the pad printing machine according to the area and volume of the printed object, and choose functions such as single-color, two-color, or rolling printing as needed. Select the dial and buttons according to the machine operation manual to determine the corresponding functions and set the process parameters.

2. Steel Plate
Generally, chrome steel is used, with a hardness of more than 60 degrees on the Rockwell scale. The etching depth of the printing plate is 0.015~0.035mm, and the thickness of the pad printing ink film is 0.004~0.008mm, which depends on the etching depth of the printing plate pattern, the hardness and shape of the printing head. Other factors such as temperature, humidity, and the environment may also cause differences in the thickness of the ink film. The size of the printing plate is measured by the area of the printed pattern. Usually, the area of the printing plate does not need to be too large, otherwise, it is difficult to fix the steel plate on the ink tray.
3. Ink Scraper
The Rockwell hardness is about 55 degrees (not exceeding the steel plate).
4. Ink
(1) Different types of ink should be used for plastic parts made of different materials.
(2) Understand the gloss, covering power, and solidification rate characteristics of the ink.
(3) The ink should not have an erosive effect on the pad printing rubber pad.
(4) The solidification rate of the ink should not be too fast, otherwise, it is easy to dry in the ink tray. In this case, it can be diluted with a solvent. If you want to accelerate the drying rate, a quick-drying agent or a blower can be used as an aid.
(5) The ink should be mixed to an appropriate viscosity. If the ink is too viscous, it will lack fluidity, resulting in printing difficulties (easy to fluff); if the ink is too thin, the printed pattern will not be clear enough in color or the lines will not be good. Therefore, the mixing of the ink is an important task.
5.Rubber Pad
The rubber pad is generally made of silicone rubber, with a Shore hardness of 25~65. A harder rubber pad generally gives a relatively better printing effect, and if it is too soft, the graphics and text will not be clear enough. The size of the pad printing rubber pad should be just sufficient. A rubber pad that is too large in volume will be a waste. Different types of plastic parts require different models of pad printing rubber pads. The shape of the pad printing rubber pad is adjusted according to the unevenness of the plastic parts to be printed. The pad printing rubber pad needs to transfer the ink on the flat steel plate to the uneven printed parts, so the end of the pad printing rubber pad should be very elastic, and the shape of the pad printing rubber pad must be suitable for the size of the plastic parts. Only in this way can the pressure on the end of the pad printing rubber pad be evenly distributed, avoiding the pad printing rubber pad from being printed obliquely on the flat surface of the plastic parts.
III. Pad Printing Process
The pad printing process is as follows:
(1) The ink scraper applies the ink to the etched recesses. When returning, the blade scrapes the ink on the steel plate back into the ink container. After the ink remaining on the etched pattern evaporates, its surface viscosity can be increased.
(2) The printing rubber pad moves downward to make contact with the etched pattern to be printed.
(3) When the printing rubber pad rises, it sucks the ink in the etched pattern onto the rubber pad.
(4) During the process of the printing rubber pad moving from the steel plate to the printed part, the solvent of the attached ink gradually volatilizes, increasing the viscosity of the ink again. The rubber pad stops at the horizontal position above the plastic part.
(5) The printing rubber pad presses down on the plastic part to be printed, transferring the attached ink to the surface of the plastic part.
(6) The printing head rises again and returns to its original position above the plastic part.
The requirements for the substrate in pad printing are the same as those in screen printing. Pad printing does not require a special heat source for drying, and natural drying or air drying is sufficient. The quality inspection of pad printing patterns is basically consistent with the requirements of screen printing.
IV. Effects of Pad Printing Patterns
(1) Color: 1 to 7 colors can be pad printed simultaneously.
(2) Gloss: Generally, only semi-gloss or matte effects can be printed.
(3) Covering Power: Due to its poor covering power, the fidelity of the color is not very good, and it is obviously interfered by the base color.
(4) Overprinting of Multiple Colors: The accuracy of overprinting depends on the accuracy of the pad printing machine used and the manufacturing accuracy of the fixture.


 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Svenska
Svenska  norsk
norsk